Introduction
The engine exhaust system catalytic converter was developed in the early 1970's when severe air pollution was prevalent, and was made mandatory in automobile manufacturing in the US in 1976. The catalytic converter or "cat" is an emission control device designed to remove un-burnt fuel in the exhaust system. In this detailed guide, we will explore the inner workings of an automotive exhaust system’s catalytic converter, breaking down how it reduces harmful emissions from your vehicle.
Why a Catalytic Converter?
Inside an automotive engine, (gasoline and diesel) the fuel combustion process is not a 100% efficient. There is always un-burnt fuel being expelled into the exhaust system and then out into the atmosphere including harmful pollutants like CO, HC, and NOx which creates air pollution.
What Does a Catalytic Converter Do?
Using the heat form the engine's exhaust output, the metals inside the catalytic converter heat up, (chemical reaction) which continues the burn process acting like an incinerator further cleaning the exhaust gases of any remaining pollutants which would normally be expelled.
How Does it Work?
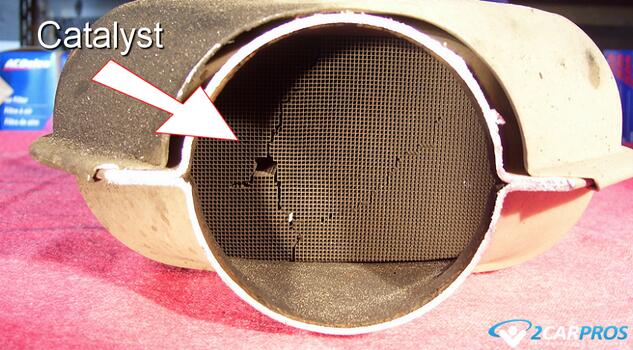
A catalytic converter is constructed with a ceramic honeycomb or wash plate which is coated with a thin layer of catalyst material, typically platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These materials are placed inside a metal container with an inlet and outlet connections. The honeycomb design provides maximum exposure to the exhaust gases.
The three primary gases targeted are:
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): A poisonous gas formed from incomplete combustion of fuel.
- Hydrocarbons (HC): Unburned fuel that contributes to smog.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Formed when the engine’s combustion temperature is too high, causing nitrogen and oxygen to react.
This is what the catalyst material looks like inside the converter, this one is broken which is why it was replaced.
Why Pumped Air?
You may have noticed that some vehicles have an air injector system which provides fresh air into the exhaust system, either before or at the catalytic converter. This AIS system is designed with an air pump, control relay, air diverter valve, air check valve and tubing, super heating the catalyst to aid in it's chemical reaction, here is what a diverter valve looks like:
Locations
In the exhaust system the catalytic converter locations will vary depending on manufacturer, some vehicles require multiple converters to help clean the exhaust gases more thoroughly. The general, the idea is the closer the catalytic converter is the engine the better it will work, utilizing the heat from the exhaust gases which is highest at the cylinder head exhaust ports. This is why some cars will have the cat integrated into the exhaust manifold.
Regulations
It is illegal to remove the or tamper with the emission control system of your vehicle which includes the catalytic converter, this is a federal offence. The catalytic converter helps vehicles comply with environmental standards like Euro 6 or EPA Tier 3 regulations.
Types of Catalytic Converters
There are several types of catalytic converters, depending on the vehicle and emission requirements:
- Two-Way Catalytic Converters: These were used in older vehicles and convert only carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into carbon dioxide and water.
- Three-Way Catalytic Converters: They convert carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides, reducing overall emissions.
- Diesel Oxidation Catalysts (DOC): Found in diesel engines, these converters focus on oxidizing carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons and often employ selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems.
Conclusion
The catalytic converter is a vital part of modern automotive exhaust systems, helping to reduce harmful emissions and protect the environment. By understanding how it works and ensuring proper maintenance, drivers can contribute to a cleaner and healthier world.
Credits
This guide knowledge base was created by the 2CarPros Team, and by Ken Lavacot: Automobile repair shop owner and certified master automobile technician of over 30 years. If you have question or need help please ask one of our experts we are happy to help. Please visit our 2CarPros YouTube Channel for additional car repairs.