Good morning,
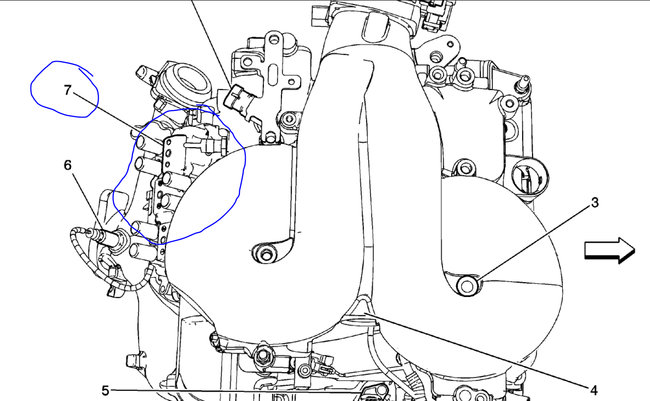
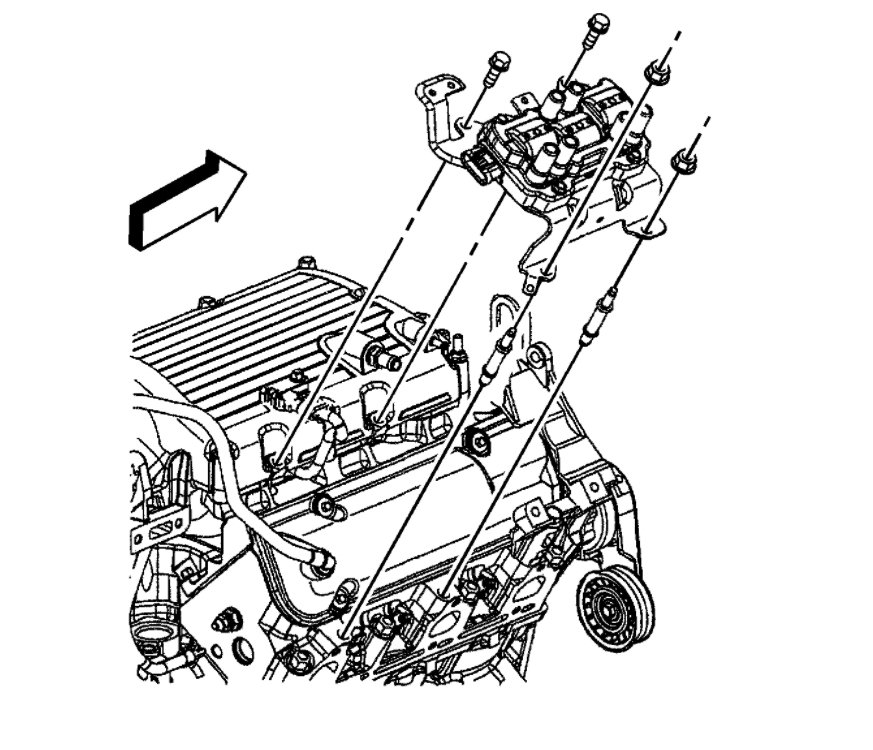
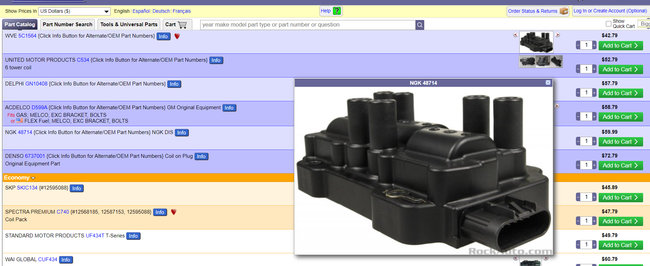
The ignition module was a common issue for this as well. It is mounted under the coils. Did you use a new one or used one?
https://www.2carpros.com/articles/engine-misfires-or-runs-rough
The other possibility is low fuel pressure. If you have low pressure from a weak fuel pump, it will misfire.
https://www.2carpros.com/articles/how-to-check-fuel-system-pressure-and-regulator
Fuel Pressure (Key "on", Engine "off") .................... 384-425 kPa (56-62 psi)
You can rent a tester at a parts store for this test.
Roy
Description of the 300 code.
DTC P0300
Diagnostic Instructions
Perform the Diagnostic System Check - Vehicle prior to using this diagnostic procedure. See: Vehicle > Initial Inspection and Diagnostic Overview
Review Strategy Based Diagnosis for an overview of the diagnostic approach.
Diagnostic Procedure Instructions provides an overview of each diagnostic category.
DTC Descriptor
DTC P0300
Engine Misfire Detected
Circuit/System Description
The engine control module (ECM) uses information from the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor in order to determine when an engine misfire is occurring, and uses information from the camshaft position (CMP) sensor in order to determine which cylinder is misfiring. By monitoring variations in the crankshaft rotation speed for each cylinder, the ECM is able to detect individual misfire events. If the ECM detects a misfire rate sufficient to cause the emission levels to exceed mandated standards, DTC P0300 sets. Under certain driving conditions, a misfire rate can be high enough to cause the 3-way catalytic converter (TWC) to overheat, possibly damaging the converter. The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will flash ON and OFF when converting overheating, damaging conditions are present and DTC P0300 is set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTCs P0016, P0101, P0102, P0103, P0107, P0108, P0116, P0117, P0118, P0120, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0125, P0128, P0220, P0222, P0223, P0335, P0336, P0608, P1516, P2101, P2119, P2120, P2122, P2123, P2125, P2135, or P2138 are not set.
DTC P0315 is not set and the engine speed is between 525-6,000 RPM.
OR
DTC P0315 is set and the engine speed is less than 1,000 RPM.
The ignition voltage is between 9-18 volts.
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) parameter is between -7 and +126°C (+19 and 259°F).
If the ECT is less than -7°C (+19°F) at engine start-up, this diagnostic is disabled until the ECT is more than +21°C (+69°F).
The fuel level is more than 10 percent.
The antilock brake system (ABS) and the traction control system (TCS) are not active or detecting rough road.
The ECM is not in fuel shut-off or decel fuel cut-off mode.
The power management is not active.
Excessive drive wheel slip is not detected.
DTC P0300 runs continuously when the above conditions are met.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM is detecting a crankshaft rotation speed variation indicating a misfire sufficient to cause emission or catalytic converter damaging levels to exceed mandated standards.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
DTC P0300 is a Type B DTC.
When the MIL is flashing, the injector may be disabled for the misfiring cylinder to protect the catalytic converter.
Depending on the conditions that set the code, the engine may go into Open Loop.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0300 is a Type B DTC.
The DTC must pass under the same conditions that were present when the DTC failed.
Diagnostic Aids
A misfire may only occur when the engine is under a load or when the engine is cold.
A misfire DTC could be caused by an excessive vibration from sources other than the engine. Inspect for the following possible sources:
A tire or wheel that is out of round or out of balance
Variable thickness brake rotors
An unbalanced drive shaft
Certain rough road conditions
A damaged accessory drive component or belt
A damaged reluctor wheel
the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn procedure may need to be performed.
The 3.5L, RPO LZE, VIN code K, E85 compatible engines only, may use either American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) gasoline with 10 percent or less ethanol content or unleaded fuel containing 85 percent ethanol, or ASTM E85. Refer to Fuel System Description.
The 3.5L, RPO LZE, VIN code K, E85 compatible engines only, over-estimation of the ethanol content will result in a rich shift of fuel trim values and under-estimation will result in a lean shift of fuel trim values. A misfire DTC may set if the learned alcohol content, Fuel Alcohol Content parameter, on the scan tool is different than the measured alcohol content in the vehicle such that values exceed failure threshold values. Refer to Fuel Composition Diagnosis. See: Computers and Control Systems > Component Tests and General Diagnostics > Fuel Composition Diagnosis
Circuit/System Verification
1. Verify that no other DTCs are set.
If a DTC is set, refer to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle. See: A L L Diagnostic Trouble Codes ( DTC ) > Diagnostic Trouble Code Descriptions
2. Engine idling, verify there is no abnormal engine noise.
If there is an abnormal engine noise, refer to Symptoms - Engine. See: Engine > Symptom Related Diagnostic Procedures > - Symptoms - Engine Mechanical
3. Observe the Misfire Current Counters with a scan tool. The Misfire Current Counters should not be incrementing. Random misfires that are not steadily incrementing may be normal.
4. If the vehicle passes the Circuit/System Verification test, then operate the vehicle within the Conditions for Running the DTC. You may also operate the vehicle within the conditions that are captured in the Freeze Frame/Failure Records List.
Circuit/System Testing
1. Verify that the following conditions do not exist:
The fuel injector wire harness electrical connectors are connected to the proper fuel injectors. Refer to Engine Controls Schematics.
Engine vacuum leaks
Fuel pressure that is too low or too high-Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis. See: Computers and Control Systems > Component Tests and General Diagnostics
Contaminated fuel-refer to Alcohol/Contaminants-in-Fuel Diagnosis. See: Computers and Control Systems > Component Tests and General Diagnostics > Alcohol/Contaminants-in-Fuel Diagnosis
Restricted exhaust system-Refer to Restricted Exhaust. See: Exhaust System > Symptom Related Diagnostic Procedures > Restricted Exhaust
If you find any of the above conditions, repair as necessary.
2. Ignition OFF, remove the spark plug wire from the spark plug and ignition coil. Inspect and test the spark plug wire for arching, cuts, rubbing on other components, and proper resistance. Refer to Spark Plug Wire Inspection and Ignition System Specifications. See: Ignition Cable > Component Tests and General Diagnostics
If a fault is found, replace the spark plug wire.
3. Install the spark plug wire to the ignition coil.
4. Install the J 26792 to the boot of the spark plug wire and ground.
Important: An erratic or weak spark is considered a no spark condition.
5. Attempt to start the engine and observe the J 26792. The spark tester should spark.
If there is no spark, refer to Electronic Ignition (EI) System Diagnosis for diagnosis of the ignition coil. See: Computers and Control Systems > Component Tests and General Diagnostics > Electronic Ignition (EI) System Diagnosis
6. Ignition OFF, remove the spark plug from the misfiring cylinder. Verify that the following conditions do not exist with the spark plug:
Gas, coolant, or oil fouled
Cracked, worn, incorrectly gapped-Refer to Spark Plug Inspection. See: Spark Plug > Component Tests and General Diagnostics
If there is a condition with the spark plug, replace the spark plug.
7. Exchange the spark plug with another cylinder that is operating correctly.
8. Operate the engine under the conditions in which the misfire occurred. This may include putting the engine under a load, turning on the A/C, seat heaters, and rear window defog. Observe the Misfire Current Counters with a scan tool. The misfire should not follow the spark plug exchange.
If the misfire follows the spark plug, replace the spark plug.
9. If all conditions test normal, test or inspect for the following:
A lean or rich fuel injector-Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis. See: Computers and Control Systems > Component Tests and General Diagnostics
An engine mechanical condition-Refer to Symptoms - Engine. See: Engine > Symptom Related Diagnostic Procedures > - Symptoms - Engine Mechanical
Repair Instructions
Spark Plug Replacement
Spark Plug Wire Replacement
Repair Verification
1. Install any components or connectors that have been removed or replaced during diagnosis.
2. Perform any adjustment, programming, or setup procedures that are required when a component or module is removed or replaced.
3. Clear the DTCs.
4. Turn OFF the ignition for 60 seconds.
5. If the repair was related to a DTC, duplicate the Conditions for running the DTC and use the Freeze Frame/Failure Records, if applicable, in order to verify the DTC does not reset. If the DTC resets or another DTC is present, refer to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle and perform the appropriate diagnostic procedure. See: A L L Diagnostic Trouble Codes ( DTC ) > Diagnostic Trouble Code Descriptions
6. To verify that the performance of the catalytic converter has not been affected by the condition that set this DTC, perform the Repair Verification for DTC P0420. Refer to DTC P0420. See: A L L Diagnostic Trouble Codes ( DTC ) > P Code Charts > P0420
Images (Click to make bigger)
Saturday, October 24th, 2020 AT 4:06 AM