DTC P0014
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The cam phasing system is a hydraulically actuated phase shifting mechanism. The powertrain control module (PCM) supplies the ignition positive driver and ground circuits. A pulse width modulated (PWM) driver controls the amount that the camshaft actuator solenoid assembly advances or retards the exhaust camshaft. The exhaust camshaft is commanded to a maximum retard position of 25 degrees. When the exhaust camshaft is retarded at the maximum rate, the duty cycle of the signal is at 100 percent. The maximum advance rate has a 0 percent duty cycle. Other than when the camshaft is at full advance, a 50 percent duty cycle is used to maintain a steady retard angle.
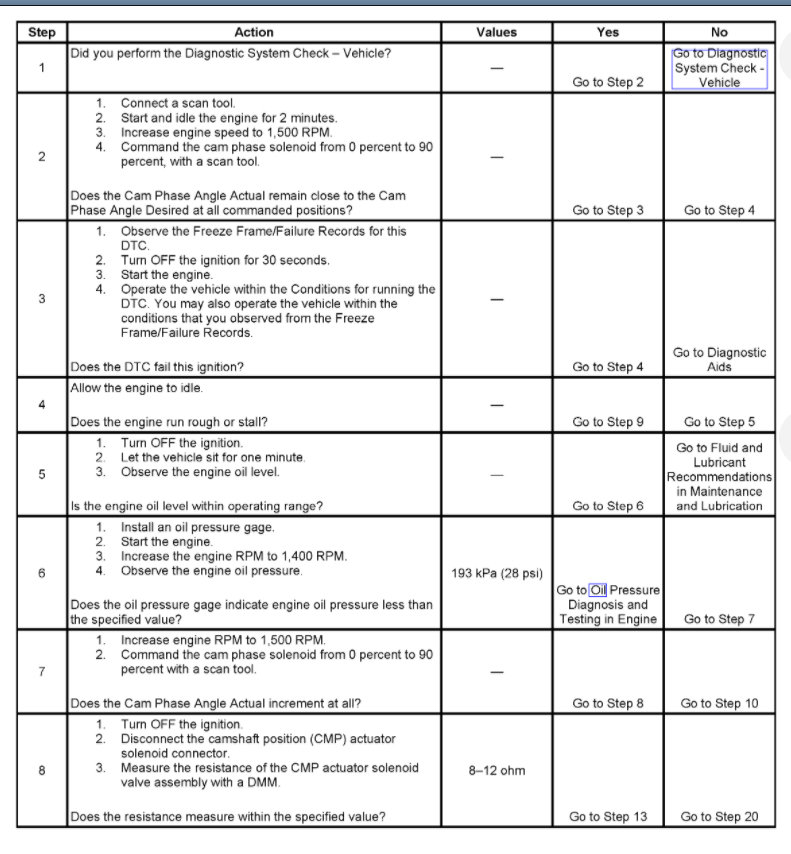
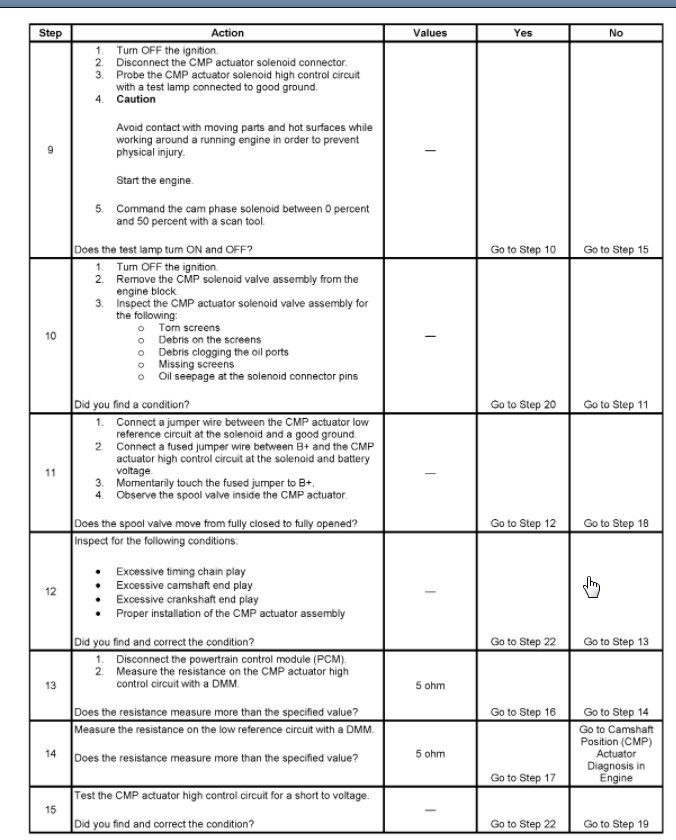
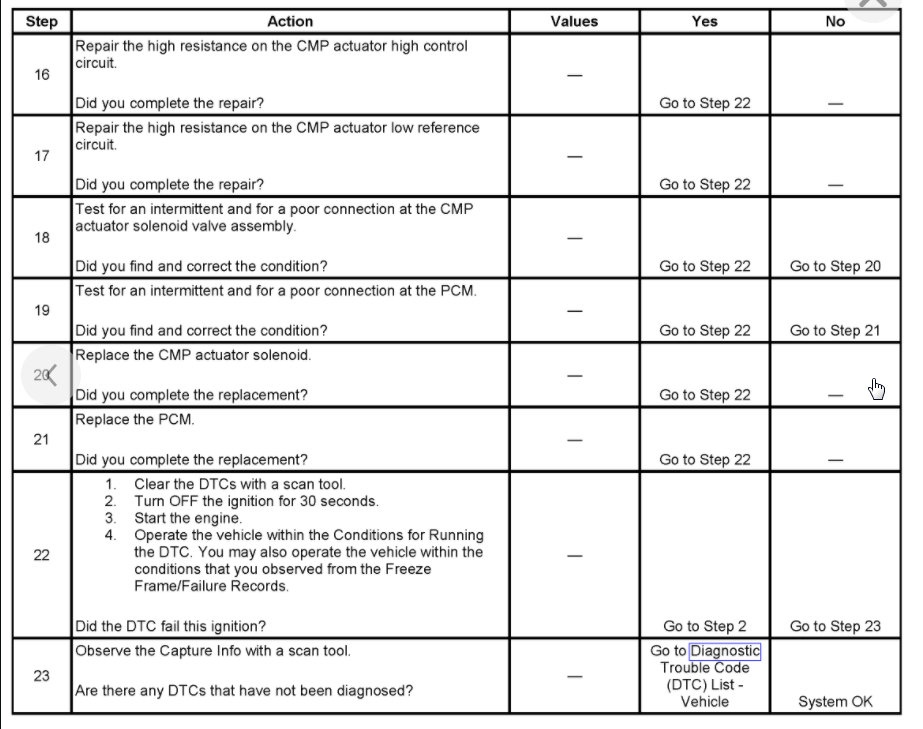
If the desired and actual cam phase angle error exceeds its tolerance value for a certain amount of time, then DTC P0014 will set.
DTC DESCRIPTOR
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTC:
DTC P0014 Exhaust Camshaft Position (CMP) System Performance
CONDITIONS FOR RUNNING THE DTC
The engine speed is greater than 1,350 RPM.
The PCM has enabled the cam phaser.
The system voltage is greater than 11 volts.
CONDITIONS FOR SETTING THE DTC
The vehicle must be driven.
The difference between the desired CAM phase angle and the actual CAM phase angle is more than 3.75 degrees.
The CAM phaser is steady for 3 seconds.
The condition is present for 3 seconds.
ACTION TAKEN WHEN THE DTC SETS
The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails.
The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records.
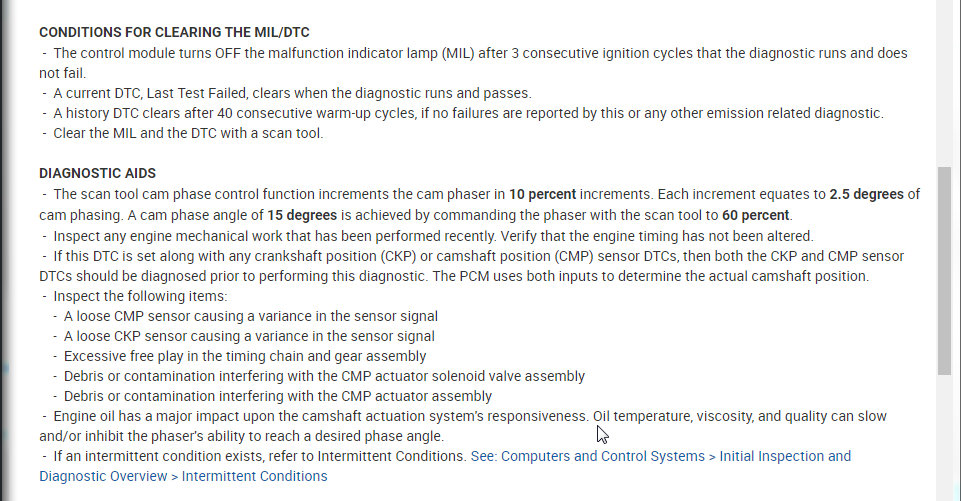
CONDITIONS FOR CLEARING THE MIL/DTC
The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail.
A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes.
A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic.
Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool.
DIAGNOSTIC AIDS
The scan tool cam phase control function increments the cam phaser in 10 percent increments. Each increment equates to 2.5 degrees of cam phasing. A cam phase angle of 15 degrees is achieved by commanding the phaser with the scan tool to 60 percent.
Inspect any engine mechanical work that has been performed recently. Verify that the engine timing has not been altered.
If this DTC is set along with any crankshaft position (CKP) or camshaft position (CMP) sensor DTCs, then both the CKP and CMP sensor DTCs should be diagnosed prior to performing this diagnostic. The PCM uses both inputs to determine the actual camshaft position.
Check the following items:
A loose CMP sensor causing a variance in the sensor signal
A loose CKP sensor causing a variance in the sensor signal
Excessive free play in the timing chain and gear assembly
Debris or contamination interfering with the CMP actuator solenoid valve assembly
Debris or contamination interfering with the CMP actuator assembly
Engine oil has a major impact upon the camshaft actuation system's responsiveness. Oil temperature, viscosity, and quality can slow and/or inhibit the phaser's ability to reach a desired phase angle.
If an intermittent condition exists, refer to Intermittent Conditions. See: Powertrain Management Computers and Control Systems Testing and Inspection Initial Inspection and Diagnostic Overview Diagnostic Strategies
Monday, January 11th, 2021 AT 11:07 AM
(Merged)